文章目录
前景概要:
上一篇文章我们安装完Wordpress,基本上也就知道一个简单的网站的发布流程,这一篇就开始部署Nextcloud,打造你的第一个私人网盘。
为什么推荐Nextcloud?
-
免费
-
部署简单
-
功能齐全,网页以及app都完美支持
Nextcloud安装最难的点就是网站配置,如果没有根据官网的配置文件的话,就可能会有如下问题:
-
安装时报错,导致连接不上数据库,无法访问页面
-
即使安装完,在
设置-概览界面,出现很多条警告
开始部署
第一步:上传Nextcloud程序到网站目录
这边以 /var/www/nextcloud 目录为例
方法1:本地下载后通过SSH软件上传到服务器
方法2:直接使用命令
wget https://download.nextcloud.com/server/releases/latest.zip
mv latest.zip /var/www
cd /var/www
unzip latest.zip添加访问权限:
chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/nextcloud
chmod -R 755 /var/www/nextcloud第二步:网站配置
这边把它的登录入口定义为: cloud.example.com
有些环境需要在
fpm/php.ini(比如php8.1的路径为:/etc/php/8.1/fpm/php.ini)配置文件中修改pathinfo:(大多数情况不需要);cgi.fix_pathinfo = 1 #去掉注释
直接在 /etc/nginx/sites-enable/ 目录下新建一个 nextcloud.conf 的配置文件:
vim /etc/nginx/sites-enable/nextcloud.conf贴入以下官方文档给出的配置文件:
upstream php-handler {
server 127.0.0.1:9000;
#server unix:/var/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sock;
}
# Set the `immutable` cache control options only for assets with a cache busting `v` argument
map $arg_v $asset_immutable {
"" "";
default "immutable";
}
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name cloud.example.com;
# Prevent nginx HTTP Server Detection
server_tokens off;
# Enforce HTTPS
return 301 https://$server_name$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
server_name cloud.example.com;
# Path to the root of your installation
root /var/www/nextcloud;
# Use Mozilla's guidelines for SSL/TLS settings
# https://mozilla.github.io/server-side-tls/ssl-config-generator/
ssl_certificate /etc/ssl/nginx/cloud.example.com.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/ssl/nginx/cloud.example.com.key;
# Prevent nginx HTTP Server Detection
server_tokens off;
# HSTS settings
# WARNING: Only add the preload option once you read about
# the consequences in https://hstspreload.org/. This option
# will add the domain to a hardcoded list that is shipped
# in all major browsers and getting removed from this list
# could take several months.
#add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=15768000; includeSubDomains; preload" always;
# set max upload size and increase upload timeout:
client_max_body_size 512M;
client_body_timeout 300s;
fastcgi_buffers 64 4K;
# Enable gzip but do not remove ETag headers
gzip on;
gzip_vary on;
gzip_comp_level 4;
gzip_min_length 256;
gzip_proxied expired no-cache no-store private no_last_modified no_etag auth;
gzip_types application/atom+xml application/javascript application/json application/ld+json application/manifest+json application/rss+xml application/vnd.geo+json application/vnd.ms-fontobject application/wasm application/x-font-ttf application/x-web-app-manifest+json application/xhtml+xml application/xml font/opentype image/bmp image/svg+xml image/x-icon text/cache-manifest text/css text/plain text/vcard text/vnd.rim.location.xloc text/vtt text/x-component text/x-cross-domain-policy;
# Pagespeed is not supported by Nextcloud, so if your server is built
# with the `ngx_pagespeed` module, uncomment this line to disable it.
#pagespeed off;
# The settings allows you to optimize the HTTP2 bandwitdth.
# See https://blog.cloudflare.com/delivering-http-2-upload-speed-improvements/
# for tunning hints
client_body_buffer_size 512k;
# HTTP response headers borrowed from Nextcloud `.htaccess`
add_header Referrer-Policy "no-referrer" always;
add_header X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff" always;
add_header X-Download-Options "noopen" always;
add_header X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN" always;
add_header X-Permitted-Cross-Domain-Policies "none" always;
add_header X-Robots-Tag "none" always;
add_header X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block" always;
# Remove X-Powered-By, which is an information leak
fastcgi_hide_header X-Powered-By;
# Specify how to handle directories -- specifying `/index.php$request_uri`
# here as the fallback means that Nginx always exhibits the desired behaviour
# when a client requests a path that corresponds to a directory that exists
# on the server. In particular, if that directory contains an index.php file,
# that file is correctly served; if it doesn't, then the request is passed to
# the front-end controller. This consistent behaviour means that we don't need
# to specify custom rules for certain paths (e.g. images and other assets,
# `/updater`, `/ocm-provider`, `/ocs-provider`), and thus
# `try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php$request_uri`
# always provides the desired behaviour.
index index.php index.html /index.php$request_uri;
# Rule borrowed from `.htaccess` to handle Microsoft DAV clients
location = / {
if ( $http_user_agent ~ ^DavClnt ) {
return 302 /remote.php/webdav/$is_args$args;
}
}
location = /robots.txt {
allow all;
log_not_found off;
access_log off;
}
# Make a regex exception for `/.well-known` so that clients can still
# access it despite the existence of the regex rule
# `location ~ /(\.|autotest|...)` which would otherwise handle requests
# for `/.well-known`.
location ^~ /.well-known {
# The rules in this block are an adaptation of the rules
# in `.htaccess` that concern `/.well-known`.
location = /.well-known/carddav { return 301 /remote.php/dav/; }
location = /.well-known/caldav { return 301 /remote.php/dav/; }
location /.well-known/acme-challenge { try_files $uri $uri/ =404; }
location /.well-known/pki-validation { try_files $uri $uri/ =404; }
# Let Nextcloud's API for `/.well-known` URIs handle all other
# requests by passing them to the front-end controller.
return 301 /index.php$request_uri;
}
# Rules borrowed from `.htaccess` to hide certain paths from clients
location ~ ^/(?:build|tests|config|lib|3rdparty|templates|data)(?:$|/) { return 404; }
location ~ ^/(?:\.|autotest|occ|issue|indie|db_|console) { return 404; }
# Ensure this block, which passes PHP files to the PHP process, is above the blocks
# which handle static assets (as seen below). If this block is not declared first,
# then Nginx will encounter an infinite rewriting loop when it prepends `/index.php`
# to the URI, resulting in a HTTP 500 error response.
location ~ \.php(?:$|/) {
# Required for legacy support
rewrite ^/(?!index|remote|public|cron|core\/ajax\/update|status|ocs\/v[12]|updater\/.+|oc[ms]-provider\/.+|.+\/richdocumentscode\/proxy) /index.php$request_uri;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+?\.php)(/.*)$;
set $path_info $fastcgi_path_info;
try_files $fastcgi_script_name =404;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param PATH_INFO $path_info;
fastcgi_param HTTPS on;
fastcgi_param modHeadersAvailable true; # Avoid sending the security headers twice
fastcgi_param front_controller_active true; # Enable pretty urls
fastcgi_pass php-handler;
fastcgi_intercept_errors on;
fastcgi_request_buffering off;
fastcgi_max_temp_file_size 0;
}
location ~ \.(?:css|js|svg|gif|png|jpg|ico|wasm|tflite|map)$ {
try_files $uri /index.php$request_uri;
add_header Cache-Control "public, max-age=15778463, $asset_immutable";
access_log off; # Optional: Don't log access to assets
location ~ \.wasm$ {
default_type application/wasm;
}
}
location ~ \.woff2?$ {
try_files $uri /index.php$request_uri;
expires 7d; # Cache-Control policy borrowed from `.htaccess`
access_log off; # Optional: Don't log access to assets
}
# Rule borrowed from `.htaccess`
location /remote {
return 301 /remote.php$request_uri;
}
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php$request_uri;
}
}我们只需查找修改以下内容:
server_name cloud.example.com; #更改为自己的域名
root /var/www/nextcloud; #更改为你的nextcloud目录
ssl_certificate /etc/ssl/nginx/cloud.example.com.crt; #SSL证书目录,一般放.pem根证书
ssl_certificate_key /etc/ssl/nginx/cloud.example.com.key; #SSL证书目录,.key私钥其他都不需要改。保存退出。
第三步:创建数据库
输入以下命令创建nextcloud数据库:
mysql
use mysql;
create database nextcloud;
exit数据库可以不创建,在程序安装时会自动创建
我的建议也是不用创建,有时候创建后反而容易出现问题
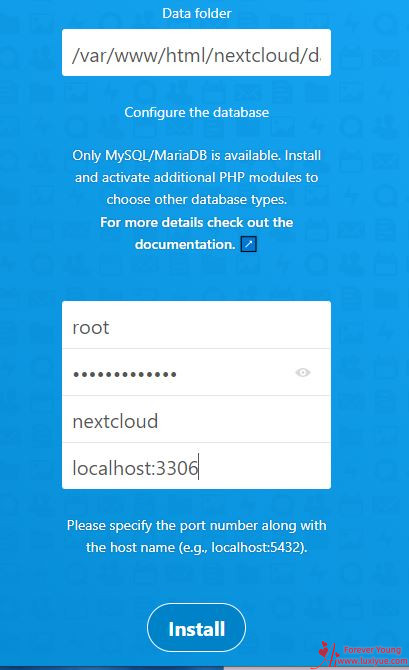
安装Nextcloud
输入你的域名访问,比如:cloud.example.com 进入到安装界面。
安装前可以确认一下Nextcloud目录权限,没权限的话安装时也会提示“服务器内部错误”
数据库地址这边要加上数据库的端口,比如MySQL默认端口是 3306 。
点击安装即可完成。
至此,NextCloud已经安装完成。
总结
Nextcloud私人网盘已经搭建完成,再回头看看,想想每一个步骤的含义,非常有意义。